India’s Green Hydrogen Revolution: Market Overview and Opportunities
India’s ₹19,744 crore Green Hydrogen Mission is creating 6 lakh jobs and targeting 5 MMT production by 2030. Here’s how this affects energy costs, air quality, and economic opportunities across the country.
That’s what I thought too—until I came across India’s ambitious Green Hydrogen Mission.
This isn’t just about high-tech labs or elite climate talk. It’s about using sunlight to power factories, running buses on water, and cutting our dependence on imported fossil fuels. In 2025, while pollution and blackouts grip our cities, green hydrogen offers a radical new possibility: What if our clean energy came from thin air?
Here’s what you’ll learn:
- How water + renewables = rocket fuel for India’s future (no PhD needed)
- Why the Indian government invested ₹19,744 crore in this mission
- Real-world projects already live (Leh’s hydrogen buses, Panipat’s breakthrough plant)
- How you fit into this story (even as a curious reader)
🔍 30-Second Snapshot
Green hydrogen in India is hydrogen fuel made using renewable energy and water through electrolysis. It emits zero carbon and is a key part of India’s ₹19,744 crore Green Hydrogen Mission aims to create around 6 lakh jobs and target 5 MMT of green hydrogen production by 2030.
Table of Contents
India’s Green Hydrogen Revolution: Market Overview and Opportunities
India’s green hydrogen sector is estimated to represent a ₹50,000+ crore market opportunity by 2030, driven by the National Green Hydrogen Mission and private sector investments of over ₹75,000 crore announced since 2021.
Market Size and Growth Projections
Current Status (2025):
- Production capacity: 0.1 MMT annually
- Investment committed: ₹85,000+ crore
- Active projects: 25+ across 12 states
- Employment: 50,000+ direct jobs
2030 Targets:
- Production target: 5 MMT annually
- Renewable capacity: 125 GW dedicated to hydrogen
- Investment pipeline: ₹8 lakh crore
- Job creation: 6 lakh positions
- Export potential: $12 billion annually
Key Economic Drivers
- Cost reduction trajectory (various industry estimates): from around $6/kg in 2023 to a possible ~$2/kg by 2030, assuming supportive policy and falling technology costs.
- Import substitution: some scenarios suggest green hydrogen could help reduce fossil fuel imports by up to ~40% over the long term.
- Export opportunities: Japan, South Korea, Germany partnerships
- Industrial transformation: Steel, fertilizer, refining sectors
Investment Breakdown by Sector
| Sector | Investment (₹ Crore) | Key Players |
|---|---|---|
| Production | 45,000 | Reliance, Adani, NTPC |
| Infrastructure | 25,000 | IOCL, BPCL, HPCL |
| Technology | 15,000 | L&T, Thermax, Ohmium |
| Export facilities | 8,000 | Ports, pipeline companies |
Source Transparency Note:
The market and investment figures in this section are drawn from publicly available government releases (MNRE, PIB), NITI Aayog assessments, and industry announcements from companies such as NTPC, Reliance, and Indian Oil. These numbers are directional estimates and may change as policies, technologies, and project pipelines evolve.
What is Green Hydrogen? India’s Clean Energy Game-Changer
Breaking It Down Without the Jargon
Let’s strip away the buzzwords.
Green hydrogen is basically hydrogen gas produced using clean electricity — like solar or wind — to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. The process is called electrolysis, and it only works when you run a current through water using a special machine called an electrolyzer.
Sounds high-tech? Kind of. But the core idea is super simple:
🌊 Water (H₂O) → Hydrogen (H₂) + Oxygen (O₂)
⚡ Powered by renewables = Green Hydrogen
Now, you might wonder — isn’t hydrogen already used in industries? Yes, but here’s the catch: most of that hydrogen is “grey” — made from fossil fuels like natural gas, releasing a ton of CO₂ in the process.
Green hydrogen, in contrast, emits zero greenhouse gases. That’s what makes it so exciting.
Honestly? I didn’t fully get the hype until I realized how different it is from regular hydrogen. One is part of the problem. The other could be the solution.
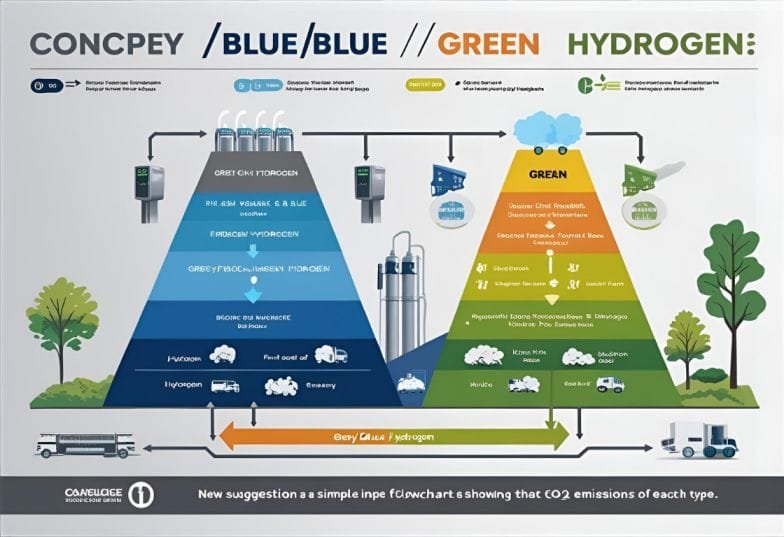
Green, Blue, Grey — What’s the Difference, and Why It Matters
You’ll hear a lot about the “colors” of hydrogen. Here’s the short version:
- Grey hydrogen: Made from natural gas, emits CO₂ — cheapest, dirtiest
- Blue hydrogen: Same as grey, but captures CO₂ using carbon capture tech — cleaner but still fossil-based
- Green hydrogen: Uses clean electricity + water — no emissions at all
It’s kind of like comparing diesel, hybrid, and electric vehicles. One pollutes, one pollutes less, and one doesn’t pollute at all — but it’s also the most expensive (for now).
In 2025, green hydrogen is still the new kid on the block. But it’s growing fast, especially in places like Europe, Japan, and yes, India.
How Green Hydrogen Is Made

Let’s quickly walk through the production process:
- You start with water (H₂O).
- A machine called an electrolyzer zaps it with electricity.
- That electricity comes from a renewable source — like solar or wind.
- The water splits into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂).
- Hydrogen is stored and used as a clean fuel. Oxygen is usually released into the air.
What makes it “green” is that none of this relies on fossil fuels. But it’s still expensive — and not yet widespread.
When I first read about this, I imagined a sci-fi lab. In reality? It’s just clean power + water + a machine — that’s it.
Why You Should Care (Even If You’re Not an Engineer)
Here’s the thing — you don’t need to be a scientist to understand why green hydrogen matters:
- It can store energy when the sun isn’t shining
- It can power heavy industries (like steel and cement) where batteries don’t work
- It can fuel buses, trains, and even planes
- It helps countries like India reduce dependence on coal and imported oil
Green hydrogen isn’t perfect — it needs water, it’s costly, and we’re still figuring out how to scale it. But if we want cleaner cities, fewer climate disasters, and reliable energy, this is one of our best bets.
Not sure I explained that perfectly — but you get the idea. Green hydrogen isn’t the whole answer. But it’s a powerful part of it.
India’s ₹19,744 Crore National Green Hydrogen Mission Explained
India’s Energy Puzzle
India’s energy story is unique — and complicated. We’re one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, but we also rely heavily on coal for electricity and import over 85% of our oil needs. That’s expensive, polluting, and vulnerable to global price shocks.
So the government had a choice: double down on fossil fuels, or leapfrog into something cleaner and smarter.
According to NITI Aayog’s 2023 Green Hydrogen Roadmap, India’s 5 MMT target is central to achieving energy independence and building a global export market.
In 2023, India launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission — a ₹19,744 crore plan to make India a global hub for green hydrogen production, use, and export.
And honestly? That’s a bold move.
🧾 India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission (2023–2030)
- 💰 Budget: ₹19,744 crore
- ⚡ Target: 5 MMT of green hydrogen/year by 2030
- 🌱 Emission Cut: 50 MMT CO₂/year
- 🏗️ RE Capacity: 125 GW for H₂ production
- 👷 Jobs: 6 lakh+
- 🌍 Export Targets: Japan, Germany, South Korea
MNRE Official Release
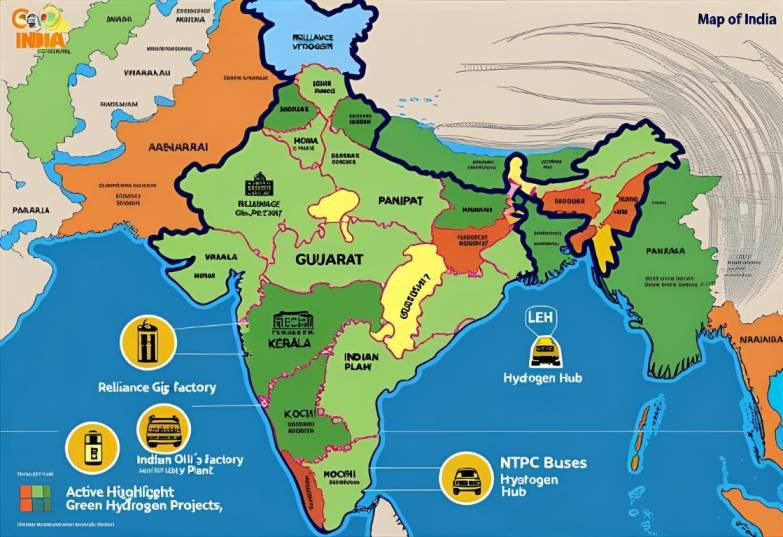
What the Mission Aims to Do
Here’s what the Green Hydrogen Mission is trying to achieve by 2030:
- Produce 5 million metric tonnes (MMT) of green hydrogen per year
- Build 125 GW of renewable energy capacity just for hydrogen production
- Reduce 50 MMT of CO₂ emissions annually
- Create over 6 lakh jobs
- Replace fossil-based hydrogen in industries like fertilizers, steel, and refineries.
- Enable export partnerships with countries like Japan, South Korea, and Germany.
For a country that still deals with load shedding and diesel gensets, this is nothing short of revolutionary.
Real Projects Already in Motion
This isn’t just a future vision. A few examples of what’s already happening:
- Reliance Industries is building giga-factories in Gujarat, including for green hydrogen
- NTPC is piloting hydrogen-fueled buses in Leh
- Indian Oil Corp has launched India’s first green hydrogen plant in Panipat
- The state of Kerala is planning a green hydrogen hub at Kochi port
- Private startups like Ohmium and Avaada are also entering electrolyzer manufacturing
These aren’t just announcements — they’re laying the groundwork for real adoption.
I used to think green hydrogen was decades away. But now I see headlines almost every week. It’s happening faster than I expected.
Why This Is a Smart Bet for India
Green hydrogen helps India:
- Cut carbon emissions
- Reduce energy imports
- Build a future-ready green economy
- Become a technology exporter rather than just a fuel importer
🔗 Want to see how green hydrogen supports a broader circular economy? Check out our post on India’s Circular Textile Systems.
It also aligns with India’s 2070 net-zero climate goal, making hydrogen a core part of our long-term survival plan.
Common Challenges of Green Hydrogen in India
Challenges of Green Hydrogen in India
I’ll be honest — the first time I read about green hydrogen, it sounded like a silver bullet. Clean, powerful, futuristic. But then I dug deeper and realized: there are still a lot of bumps on this road.
No one’s pretending green hydrogen is perfect. The biggest challenges are exactly why it’s still not mainstream. Let’s break them down.
The Cost Is Still Too High
Right now, green hydrogen costs around ₹300–400 per kilogram in India. That’s 2–3 times more expensive than grey hydrogen (which is made using fossil fuels). And unless we can bring the price down, industries won’t switch.
Why is it so expensive?
- Electrolyzers are costly and mostly imported.
- Solar and wind power aren’t always available 24/7
- Hydrogen storage and transport tech is still developing
- We don’t yet have economies of scale
The good news? With more demand, manufacturing, and innovation, these costs are expected to fall by up to 50% in the next decade.
Storage and Safety Issues
Hydrogen is the lightest element on Earth, which makes it hard to store and transport.
- It can leak easily from containers
- It’s highly flammable (though manageable with proper systems)
- Compressing or liquefying it takes a lot of energy
- India doesn’t yet have a full-scale hydrogen pipeline or transport network
I once saw a debate where someone said hydrogen was “too leaky to be practical.” I get that concern now. But every new tech starts clunky. So did solar. So did electric cars.
Water Usage in a Water-Stressed Country
One hidden cost? Green hydrogen uses water — about 9 liters for every 1 kg of hydrogen.
In water-scarce regions of India, this could become a serious constraint. That’s why researchers are working on:
- Using non-potable water (like seawater or treated wastewater)
- Improving electrolyzer efficiency
- Co-locating plants with desalination or water recycling units
Policy & Skill Gaps
Even with the Green Hydrogen Mission in place, challenges remain:
- Lack of clear safety and transport regulations
- Shortage of trained engineers and technicians
- Limited awareness at the industry level
India needs to build an entire ecosystem, not just the fuel. That means partnerships, education, investment, and patience.
7 Major Green Hydrogen Projects Live in India (2025)
From Headlines to Reality — What’s Already Happening
If you think green hydrogen is just an idea in a government whitepaper, think again. Across India, early projects are quietly moving from pilot to practical. And that’s a big deal.
Here are just a few real-life examples that show what’s possible:
NTPC Leh Hydrogen Bus Project
India’s largest power producer, NTPC, launched a pilot program in Leh, Ladakh, running hydrogen-fueled buses at high altitudes.
- Why Leh? It’s remote, diesel is expensive, and air pollution hits hard.
- Result: Zero tailpipe emissions, smooth operation even in tough terrain.

Imagine clean buses climbing Himalayan roads without a puff of smoke — it’s real.
Indian Oil Panipat Green Hydrogen Plant
Indian Oil Corporation set up India’s first green hydrogen plant at its refinery in Panipat, Haryana. It uses solar-powered electrolysis to generate hydrogen for internal use.
- Focus: Replacing grey hydrogen used in refining with green hydrogen
- Impact: Cuts CO₂ emissions while keeping operations efficient
Reliance Gujarat Giga-Factory
Reliance Industries is investing billions in a green energy mega-complex in Gujarat, including:
- Electrolyzer production
- Solar and wind farms
- Green hydrogen fuel systems
Mukesh Ambani’s goal? To produce green hydrogen at $1/kg — a global game-changer.
Startups Like Ohmium and Avaada
- Ohmium (Karnataka): Makes electrolyzers in India for Indian needs
- Avaada (Maharashtra): Developing integrated green hydrogen projects
What’s exciting? These aren’t just global giants — Indian startups are jumping in too.
Green Hydrogen vs Grey & Blue Hydrogen: What’s the Difference?
Different People, Different Possibilities
Let’s get real for a moment. When people hear about green hydrogen, their first reaction is usually:
“Cool… but how does this affect me?”
And honestly? That’s fair.
Green hydrogen won’t replace your home LPG cylinder tomorrow. But it can shape the systems around you — your commute, the products you buy, even the air you breathe.
Depending on where you live or work, hydrogen might play a very different role in your life.
Urban Professionals
If you live in a city like Delhi, Mumbai, or Bengaluru:
- Buses and public transport may soon run on hydrogen fuel cells
- E-commerce trucks could switch to hydrogen over diesel
- Industries nearby (like steel or chemicals) may clean up their act using green hydrogen
- Cleaner industrial zones mean better urban air quality (goodbye, PM2.5 smog)
Students and Young Engineers
Studying renewable energy, chemical engineering, or policy? You’re in the right place.
- Green hydrogen needs talent in R&D, policy design, manufacturing, and safety systems
- New careers are forming around hydrogen fuel, electrolyzers, and clean mobility
- Colleges are starting hydrogen research hubs and projects — a great place to start
Rural or Semi-Urban Areas
You might not see a hydrogen car in your village yet — but:
- Hydrogen could power mini-grids or agri-processing units
- Local water recycling + solar = decentralized clean hydrogen plants
- It could offer clean jobs without urban migration
I used to think climate tech was only for “big cities.” But hydrogen is surprisingly flexible — it can meet big industry needs and small rural ones. That’s powerful.
How Green Hydrogen Helps India Meet Net Zero Goals
It’s Not Just About Energy — It’s About Independence
Here’s the thing. India imports over 85% of its oil and nearly half its natural gas. That’s a huge financial and geopolitical burden. Every price spike or global conflict hits us hard.
Green hydrogen is India’s chance to flip the script. To make clean energy in India, for India, using sunlight, wind, and water.
Climate Goals Need Backup
Even if we max out solar, wind, and batteries, some sectors still emit huge amounts of CO₂ — especially:
- Steel and cement
- Fertilizer production
- Long-haul transport and shipping
These are hard to decarbonize. Batteries can’t do it alone. Hydrogen can step in.
Jobs and Innovation for the Next Gen
The global green hydrogen market could be worth $500+ billion by 2050. That’s not a trend — that’s an economy.
India could:
- Become a hub for electrolyzer manufacturing
- Export green hydrogen to countries like Japan, South Korea, and Germany
- Create thousands of jobs in engineering, operations, and maintenance
Honestly? It’s easy to get cynical about climate action. But green hydrogen gives me hope — not because it’s perfect, but because it shows we’re still trying, still innovating, still dreaming forward.
Start Where You Are — Tiny Steps That Matter
You Don’t Need a Hydrogen Car to Make a Difference
Let’s be honest — most of us aren’t going to install a hydrogen fuel cell in our backyard.
We’re not powerless. Supporting green hydrogen can start small—right where you are.
🌿 Curious about other green tech solutions that cool Indian cities? Explore our guide to Urban Cooling Strategies Using Nature-Based Solutions.
Micro-Actions with Macro Impact
- Talk about it: Mention green hydrogen in your classroom, group chat, or team meeting. Awareness spreads action.
- Follow real projects: Track updates from NTPC, Reliance, or startups like Ohmium. Be informed.
- Support clean tech: Choose brands, policies, or leaders that back renewable innovation.
- Stay curious: Read more. Ask questions. Watch for what’s being piloted in your state or city.
I started by just reading articles and following hydrogen news on LinkedIn. Then it showed up in a job brief, and suddenly it wasn’t “just tech” — it was my future.
Small Steps Add Up
You’re not expected to solve the energy crisis. But showing up — even with interest — matters more than you think. Because movements grow when enough of us care, even quietly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What exactly is green hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is hydrogen gas made using renewable energy (like solar or wind) and water. It’s different from “grey” hydrogen, which is made using fossil fuels. Green = clean.
Q2: How is hydrogen different from electricity or batteries?
Hydrogen stores energy chemically, while batteries store it electrically. Hydrogen is better for heavy-duty use (like trucks, factories, or ships), where batteries can fall short.
Q3: Is green hydrogen safe? Isn’t hydrogen explosive?
Yes, hydrogen is flammable — just like petrol or cooking gas. But with proper handling and infrastructure, it can be safely stored and used. It’s already used in many industries.
Q4: Can I use green hydrogen at home?
Not directly. Green hydrogen today is mainly for industry, transport, and power systems. But its growth could improve energy access and air quality around you — especially in cities.
Q5: Why is India so focused on green hydrogen?
It helps India reduce oil imports, meet climate goals, and build a self-reliant energy system. It’s also a chance to lead in a new global market — from tech to trade.
Q6: What’s stopping green hydrogen from going mainstream?
Mainly cost and infrastructure. Green hydrogen is still expensive to make, and we need better systems to store and use it. But prices are falling fast, and governments are investing heavily.
Conclusion: A Future Worth Fueling
When I first heard about green hydrogen, it felt distant — like something meant for labs, not for real life. But the deeper I looked, the more I saw how personal it is.
India’s green hydrogen push isn’t just about meeting global climate targets. It’s about cleaner air, energy freedom, future jobs, and a shot at doing things differently. We’ve spent decades relying on fossil fuels that choke our lungs and drain our economy. Green hydrogen offers a reset — not a perfect one, but a promising one.
Maybe you won’t see a hydrogen-powered bus tomorrow. Maybe it’ll take a few more years. But the shift is already happening — in policy rooms, in factories, in student labs, in quiet corners of the country where change begins.
So wherever you are — curious, skeptical, hopeful — know this: you’re part of the story. Just by paying attention. Just by asking what comes next.
And that? That matters more than you think.
Author Bio
Written by Soumen Chakraborty, Founder of Ecoplanet and Environmental Researcher focusing on India’s pollution and sustainable development.
What Is Green Hydrogen in India? Discover how this clean energy game-changer works and why it’s vital for shaping the nation’s climate future.
📚 Learn More
Last updated: August 15, 2025
Some of the images in this story were created using AI to help illustrate key concepts more clearly. They’re meant to support learning—not simulate real-world scenes.
- Groundwater Pollution in India (2025): Nitrate, Fluoride & Arsenic Contamination Explained - December 1, 2025
- How Air Purifiers Work: Real Science, Real Effectiveness & India-Focused 2025 Guide - November 20, 2025
- Indoor Air Pollution in India (2025 Guide): Hidden Sources & Health Risks - November 16, 2025

