Introduction
Air pollution is commonly described as a condition in which substances are present in the atmosphere at concentrations that differ from natural background levels. Within scientific and institutional literature, the term functions as a descriptive classification, rather than a judgment about consequences or severity. Definitions focus on what constitutes a pollutant, how it is identified, and how it is distinguished from the normal chemical composition of air.
This educational explainer examines air pollution strictly at the level of foundational definitions. It outlines how the concept is framed across environmental science, atmospheric research, and institutional monitoring systems, without extending into health effects, policy evaluation, or mitigation discussions. Emphasis is placed on terminology, classification logic, and the conceptual boundaries that separate definition from interpretation.

Understanding how air pollution is defined provides essential context for later analysis in research, governance, and comparative environmental studies. However, definitions alone do not explain impacts, risks, or responses. They instead establish a shared reference point that allows observations to be described consistently across regions, time periods, and scientific disciplines.
The sections that follow clarify how air pollution is characterized, how pollutants are grouped and described, and why definitions vary depending on measurement capabilities and environmental context.
Defining Air Pollution in Scientific and Institutional Contexts
In environmental science, air pollution is defined by comparison. Atmospheric air has a known natural composition dominated by nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and trace gases. Within this framework, air pollution refers to the presence of additional substances, or altered concentrations of naturally occurring substances, that deviate from background atmospheric conditions as documented through observation and measurement.
Scientific definitions emphasize description rather than evaluation. A substance is considered an air pollutant based on its physical or chemical presence in the air, not on inferred consequences. This distinction allows researchers to document atmospheric conditions without embedding assumptions about harm, regulation, or urgency. As a result, definitions are designed to be stable across contexts, even as interpretations evolve.
Institutional definitions often align closely with scientific usage while introducing standardized terminology to support monitoring and reporting. Organizations such as the World Health Organization and the United Nations Environment Programme describe air pollution in terms of contaminating substances in the ambient environment, while avoiding prescriptive language. These definitions function as reference points for data collection rather than as evaluative statements.
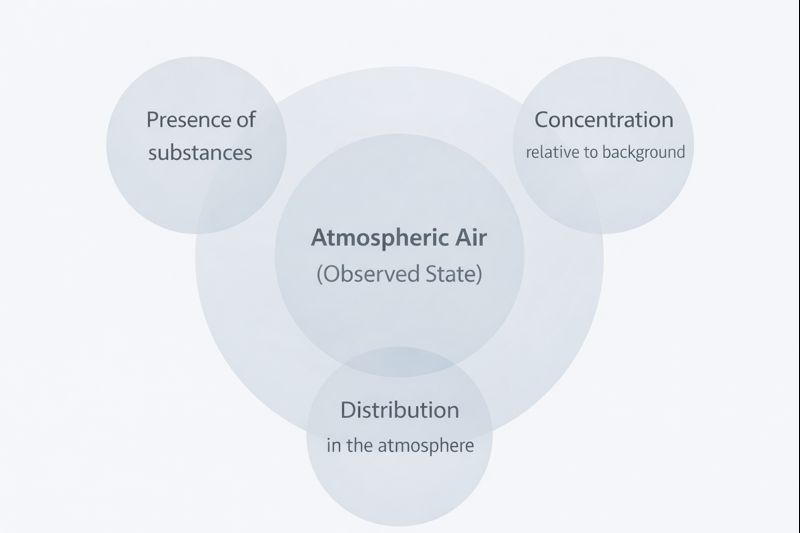
Variation across institutions is primarily linguistic rather than conceptual. Differences typically reflect administrative scope, measurement capabilities, or reporting mandates. Despite this variation, most definitions converge on three core elements: the presence of substances, their concentration relative to background levels, and their persistence or distribution within the atmosphere.
Categories and Classification of Air Pollutants
Air pollutants are commonly classified using systems that describe how substances enter or behave in the atmosphere. One widely used conceptual distinction separates primary pollutants from secondary pollutants. Primary pollutants are defined as substances released directly into the air from identifiable processes or sources. Secondary pollutants, by contrast, are defined by their formation within the atmosphere through chemical or physical transformation.
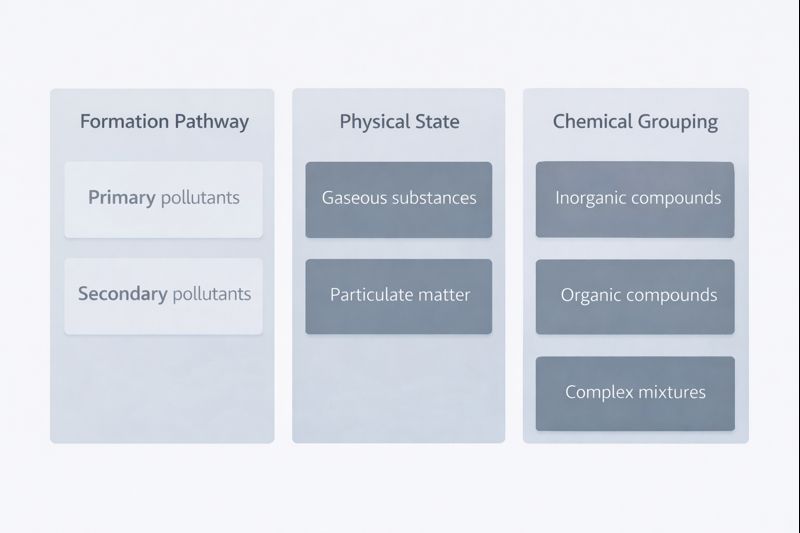
Another foundational classification approach is based on physical and chemical characteristics. Gaseous pollutants are defined by their molecular state and dispersion behavior, while particulate matter is defined by the presence of solid or liquid particles suspended in air. Particulate matter is further described using size-based categories, which function as measurement descriptors rather than indicators of effect.
Chemical composition also plays a role in classification. Inorganic compounds, organic compounds, and complex mixtures are grouped to support analytical consistency. These categories assist researchers in identifying substances using laboratory and field instruments, but they do not imply uniform behavior across environments.
Source-based groupings are sometimes used descriptively to indicate whether substances originate from natural processes or human-associated activities. However, scientific literature consistently notes that such distinctions are not absolute. Many substances occur across both categories, and classification serves analytical clarity rather than categorical separation.
Spatial, Temporal, and Environmental Context of Air Pollution
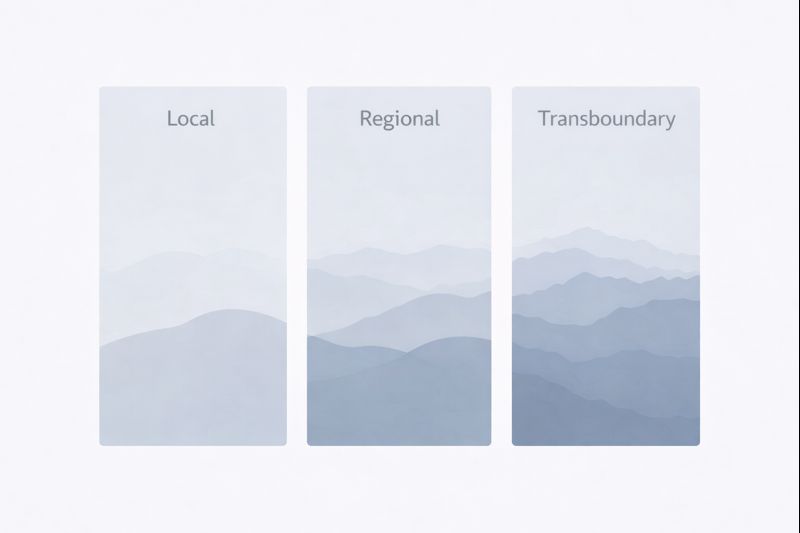
Definitions of air pollution are inseparable from spatial and temporal context. Air pollution may be described at local, regional, or transboundary scales, depending on how substances disperse through atmospheric circulation. These spatial descriptors clarify where pollutants are observed, not where they originate or accumulate.
Temporal framing is similarly descriptive. Air pollution can be characterized as episodic, seasonal, or persistent based on observation intervals. Short-term presence and long-term atmospheric residence are treated as definitional attributes that inform how air pollution is recorded and compared over time.
Environmental context further shapes how air pollution is defined. Atmospheric conditions interact continuously with land surfaces, water bodies, and climatic systems. Definitions acknowledge these interactions without extending into causal interpretation. The focus remains on documenting presence and movement within the atmospheric system.
This contextual framing allows definitions to remain flexible across geographic regions and environmental conditions. It also explains why the same substance may be classified differently depending on observational scale or measurement resolution.
Conceptual Boundaries and Limitations of Definitions
A key limitation of air pollution definitions is their deliberate separation from standards and thresholds. While measurement systems often rely on numerical benchmarks, these benchmarks are not intrinsic to the definition itself. Definitions describe what is present, whereas thresholds describe how observations are interpreted within specific regulatory or analytical frameworks.

Definitions are also shaped by scientific capability. As monitoring instruments become more sensitive, substances previously undetectable may become definable within atmospheric datasets. This does not indicate a change in atmospheric reality, but rather an expansion of observational scope.
Context dependence introduces further limitation. Definitions that function effectively in one region or research setting may require adaptation elsewhere due to climatic variation, altitude, or background composition. As a result, air pollution definitions are best understood as structured descriptors rather than fixed universal statements.
Importantly, definitions do not explain consequences. They establish a shared language that supports subsequent analysis, comparison, and interpretation, while remaining intentionally neutral with respect to outcomes.
Conclusion
Air pollution, when approached at the level of definition, is best understood as a descriptive concept grounded in atmospheric observation rather than interpretation. Scientific and institutional frameworks define it through the presence, concentration, and behavior of substances in air relative to documented background conditions. These definitions prioritize consistency, measurability, and comparability across regions and time periods.
The classification systems applied to air pollution—whether based on formation pathways, physical state, chemical composition, or observational context—serve analytical purposes. They provide structured ways to describe complex atmospheric mixtures without implying severity, impact, or intent. Spatial and temporal descriptors further situate air pollution within dynamic environmental systems, acknowledging variability without assigning consequence.
Equally important are the boundaries of these definitions. Air pollution definitions are intentionally distinct from standards, thresholds, and evaluative judgments. They evolve alongside measurement capabilities and scientific understanding, reflecting advances in observation rather than changes in underlying phenomena.
Taken together, these foundational definitions establish a shared conceptual language. They enable researchers, institutions, and comparative studies to document and communicate atmospheric conditions with clarity, while leaving questions of impact, governance, and response to separate analytical stages beyond the scope of definition itself.
References
- World Health Organization (2021). WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Global Update. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240034228
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Air Pollution in the Context of Atmospheric Systems. UNEP, Nairobi. https://www.unep.org/explore-topics/air
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Cambridge University Press. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Basic Information about Air Quality and Pollutants. EPA, Washington, DC. https://www.epa.gov/air-quality-management-process/basic-information-air-quality
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Air Pollution: Concepts, Terminology, and Classification. EEA, Copenhagen. https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/air
- Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), Government of India. National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP): Conceptual Overview. New Delhi. https://cpcb.nic.in/national-air-quality-monitoring-programme-namp/
Author Bio
The author is an independent educational researcher focused on environmental systems and atmospheric science, with an emphasis on air pollution as a population-level and institutional subject. Their work centers on explaining foundational concepts, terminology, and classification frameworks using publicly available data and authoritative sources.
All content is written in a neutral, academic style intended for students, educators, and policy-aware readers. Explanations are descriptive rather than advisory and avoid professional, medical, or regulatory guidance. The author’s approach prioritizes clarity, source-based framing, and alignment with international research and institutional definitions.
This definitional overview supports broader analysis of air pollution causes, impacts, and policy contexts in India.

